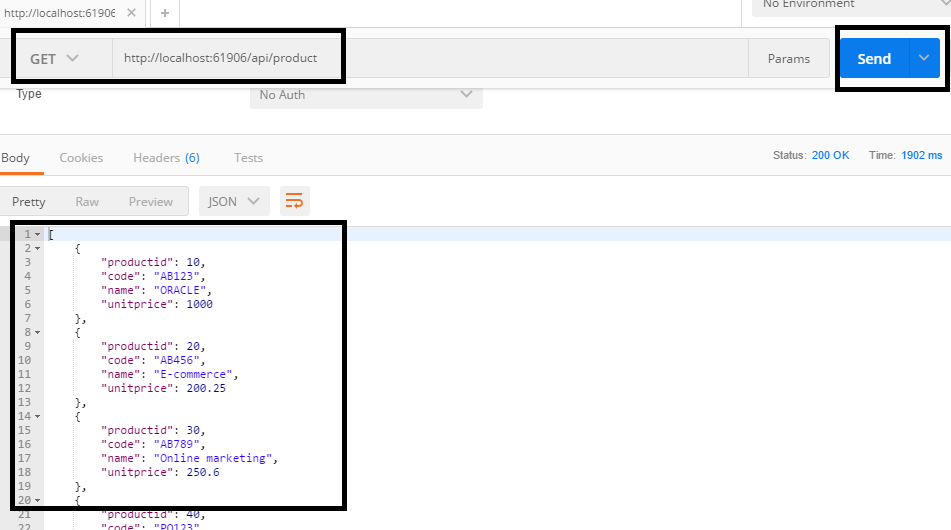
Oct 9, 2018 - Sections: “How to download zip files in ASP Net Core” is published by Xavier Penya. Today, we are announcing.NET Core 2.0 Preview 1. It is the first public release of.NET Core 2.0. We have great improvements that we want to share and that we would love to get your feedback on. You can develop.NET Core 2.0 apps with Visual Studio 2017 Preview 15.3. Download files from url to local device in.Net Core. Ask Question 9. In.Net 4.0 I used WebClient to download files from an url and save them on my local drive. But I am not able to achieve the same in.Net Core. WebClient is not available in.NET Core. (UPDATE: It is from 2.0) The usage of HttpClient in the System.Net.Http is therefore.
.NET Core provides a fast and modular platform for creating server apps that run on Windows, Linux, and macOS. Use Visual Studio Code with the C# extension to get a powerful editing experience with C# IntelliSense (smart code completion) and debugging. Entity Framework Core with Angular 2. Let’s start how to work with entity framework Core with Angular 2 and ASP.NET Core 2.0. Download Sample Project “Entity Framework with Angular 2 and ASP.NET Core 2.0” Step # 1 – Create a New Project. If you don’t know how to create a new project using Angular2 and ASP.NET Core 2.0, then Click here.
ASP.NET Core MVC model binding provides IFormFile interface to upload one or more files. Upload file in ASP.NET Core MVC, upload file in ASP.NET Core, upload file in ASP.NET Core 2.0, upload file in MVC. PowerShell 2.0 continues to work on Windows 2008 R2 SP1 Server Core when.NET Framework 4 is installed (utilizing the installed.NET Framework 3.5.SP1). PowerShell 2.0 does not use.NET Framework 4, so there is no support for writing.NET Framework 4 cmdlets and runing them on Windows 2008 R2 server core.
The ASP.NET team is proud to announce general availability of ASP.NET Core 2.0. This release features compatibility with .NET Core 2.0, tooling support in Visual Studio 2017 version 15.3, and the new Razor Pages user-interface design paradigm. For a full list of updates, you can read the release notes and you can check the list of changed items in the ASP.NET Announcements GitHub repository for a list of changes from previous versions of ASP.NET Core. The latest SDK and tools can be downloaded from https://dot.net/core. Read the .NET Core 2.0 release announcement for more information and watch the launch video:
With the ASP.NET Core 2.0 release we’ve added many new features to make building and monitoring web apps easier and we’ve worked hard to improve performance even more. More details about these features are available in our follow up post about ASP.NET Core features.
Updating a Project to ASP.NET Core 2.0
ASP.NET Core 2.0 runs on both .NET Framework 4.6.1 and .NET Core 2.0, so you will need to update your target framework in your project to netcoreapp2.0 if you were previously targeting a 1.x version of .NET Core.
Next, we recommend you reference the new Microsoft.AspNetCore.All metapackage instead of the collection of individual Microsoft.AspNetCore.* packages that you previously used. This new metapackage contains references to all of the AspNetCore packages and maintains a complete line-up of compatible packages. You can still include explicit references to specific Microsoft.AspNetCore.* package versions if you need one that is outside of the lineup, but our goal is to make this as simple a reference as possible.
What happens at publication time? We know that you don’t want to publish the entire AspNetCore framework to your target environments, so the publish task now distributes only those libraries that you reference in your code. This tree-pruning step should help make your publish process much smoother and easier to distribute your web applications.
More information about the features and changes you will need to address when migrating from ASP.NET Core 1.x to 2.0 can be found in our documentation.
Introducing Razor Pages
With this release of ASP.NET Core, we are introducing a new coding paradigm that makes writing page-focused scenarios easier and simpler than our current Model-View-Controller architecture. Razor Pages are a page-first structure that allow you to focus on the user-interface and simplify the server-side experience by writing PageModel objects.
If you are familiar with how to configure your ASP.NET Core Startup class for MVC, then you already have the following lines in your Startup class:
Surprise! The AddMvc and UseMvc configuration calls in your Startup class also activate the Razor Pages feature. You can start writing a Razor Page by placing a new cshtml file called Now.cshtml in the Pages/ top-level folder of your application. Let’s look at a simple page that shows the current time:
This looks like a standard MVC View written in Razor, but also has the @page directive at the top to indicate that this is a stand-alone Razor Page built with that paradigm. Non stop mp3 songs download. HtmlHelpers, TagHelpers, and other .NET Code is available to us in the course of the page. We can add methods just as we could in Razor views, by adding a block level element called @functions and writing methods into that element:
We can build more complex structures by taking advantage of the new PageModel object. The PageModel is an MVVM architectural concept that allows you to execute methods and bind properties to the Page content that is being rendered. We can enhance our sample by creating a NowModel.cshtml.cs C# class file in the Pages folder with this content:
With this class that inherits from PageModel, we can now do more complex interactions and build out a class that can be unit tested. In this case, we are simply loading the LastModified property on the Now page and setting that to the LastModified property. Also note the OnGet method to indicate that this PageModel handles the HTTP GET verb. We can update our Razor Page with the following syntax to start using the PageModel and output the last update date:
For more information, check out the ASP.NET Core documentation on getting started with Razor Pages.
Updated Templates and SPA Templates
The templates that ship with ASP.NET Core have been enhanced to not only include a web application that is built with the MVC pattern, but also a razor pages web application template, and a series of templates that enable you to build single-page-applications (SPA) for the browser. These SPA templates use the JavaScript Services functionality to embed NodeJS within ASP.NET Core on the server, and compile the JavaScript applications server-side as part of the .NET build process.
These same templates are also available out of the box at the command-line when you type dotnet new:
DbContext Pooling with Entity Framework Core 2.0
Many ASP.NET Core applications can now obtain a performance boost by configuring the service registration of their DbContext types to use a pool of pre-created instances, avoiding the cost of creating new instance for every request. Try adding the following code to your Startup/ConfigureServices to enable DbContext pooling:
You can read more information about the updates included in Entity Framework Core 2.0 online in their announcement post.
Monitor and Profile with No Code Changes and Application Insights
ASP.NET Core 2.0 runs with no modifications necessary on Azure App Service and comes with integrations that provide performance profiling, error reporting, and diagnostics from Azure Application Insights. In Visual Studio 2017, right-click on your project and choose “Add – Application Insights Telemetry” to start collecting data from your application. You can then review the performance of your application including all log messages directly within Visual Studio 2017.
That’s nice when you’re developing your application, but what if your application is already in Azure? We’ve got support in the Azure portal to start profiling and debugging, and it starts when you first publish your application and navigate to the cloud portal for your new app service. Azure will prompt you with a new purple banner indicating that Application Insights for monitoring and profiling is available
When you click through that banner, you will create an Application Insights service for your application and attach those features without recompiling or redeploying. Shortly afterwards, your new Application Insights service will start reporting data about the activity captured.

It even shows the number of failed requests and errors in the application. If you click through that area, you’ll see details about the failed requests:
There is a System.Exception thrown, and identified at the bottom of the screen, if we click through that reported exception, we can see more about each time that exception was thrown. When you click through a single instance of those exceptions, you get some neat information about the exception including the call stack:
Snapshot debugging in Application Insights now supports ASP.NET Core 2.0. If you configure snapshot debugging in your application, then the “Open Debug Snapshot” link at the top will appear and show the complete call stack and you can click through method calls in the stack to review the local variables:
Nice! We can go one step further and click that “Download Snapshot” button in the top corner to start a debug session in Visual Studio right at the point this exception was thrown.
What about the performance of these pages? From the Application Insights blade, you can choose the Performance option on the left and dig deeper into the performance of each request to your application.
There are more details available in our docs about performance profiling using Application Insights.
If you want the raw logs about your application, you can enable the Diagnostic Logs in App Service and set the diagnostic level to Warning or Error to see this exception get thrown.
Finally, choose the Log Stream on the left and you can watch the same console that you would have on your developer workstation. The errors and log messages of the selected severity level or greater will appear as they are triggered in Azure.
All of the Application Insights features can be activated in ASP.NET Core without rebuilding and deploying. Snapshot debugging requires an extra step and some code to be added, and the configuration is as simple as an extra NuGet package and a line in your Startup class.
You can learn more about Application Insights Telemetry in our online documentation.
Razor Support for C# 7.1
The Razor engine has been updated to work with the new Roslyn compiler and that includes support for C# 7.1 features like Default Expressions, Inferred Tuple Names, and Pattern-Matching with Generics. To use C #7.1 features in your project add the following property in your project file and then reload the solution:
C# 7.1 is itself in a preview state, and you can review the language specification for these features on their GitHub repository.
Simplified Application Host Configuration
Host configuration has been dramatically simplified, with a new WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder included in the default ASP.NET Core templates that automatically allocates a Kestrel server that will attempt to run on IIS if it is available, and configures the standard console logging providers. Your Program.cs file is simplified to only this content:
Net Core 2.1
That reduces the possibility of accidentally breaking some of the standard configuration that most developers were not altering in their ASP.NET Core applications. Why make you write the same boilerplate code over and over, when it could be simplified to 3 lines of code?
Summary
These updates in ASP.NET Core 2.0 provide new ways to write your applications and simplify some of the operational process of managing a production application. A word of thanks to our .NET Community for their feedback, issues, and contributed source code on GitHub. They’ve really been a huge help in delivering this new version of ASP.NET Core. We encourage you to download the latest .NET Core SDK from https://dot.net/core and start working with this new version of ASP.NET Core. You can watch the launch video for .NET Core 2.0 and ASP.NET Core 2.0 at: https://aka.ms/dotnetcore2launchvideo
In my previous post, I have mentioned how to create Serverless .Net Core application which you can find here and you can find my all .Net Core posts here.
In this post, I will explain how to hostdeploy your .Net Core 2.0 application to IIS.
prerequisite:
- Visual studio 2017 community edition, download here
- .Net Core 2.0 SDK from here (I have written a post to install SDK here)
- Make sure you have enabled the Web Server (IIS) role and established the role services
Install .NET Core Windows Server Hosting Bundle
Since .Net Core is a new framework, at this moment IIS is not aware of how to run .Net Core applications. So we need to inform IIS to set up an environment for the .Net Core applications.
For this, we need to install .Net Core Windows Server Hosting bundle which will install the .NET Core runtime, libraries, and the ASP.NET Core module for IIS.
Please note that this is a very important step and you must install the bundle before you publish the application on IIS.
You can download it from here(download will start once you click the link):
Wait till the installation is over:
Once the installation is completed, either restart your system or run below commands in sequence in command prompt:
- net stop was /y
- net start w3svc
The first command will stop the World Wide Web publishing service and the second command will start the service again.
Create the Web application using .Net Core 2.0 template in VS 2017
Once you have all these installed, open your Visual Studio 2017 -> Create New Project -> Select Core Web application: Atv repair manuals free. download full.
Click on Web Application in next window and then click on Ok:
Visual Studio will create a well-structured application for you.
Right click on the solution and click on Publish:
In next window, click on Folders and give the folder path. I created Publish folder under wwwroot folder:
It will publish the application on the above-mentioned path:
Create Website on IIS
Open your IIS Manager and add new website:
This package installs an updated version of the Microsoft Windows 7, Vista and XP device driver for the Realtek Ethernet that comes preinstalled in your. Lenovo realtek network controller driver. Click Start, Right-click my computer and select manage. In Device manager, click Network adapters. In Device manager,double click Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller. Click the Driver tab.Then you will see the driver version. Realtek Ethernet Controller Driver for Microsoft Windows 7 (32-bit, 64-bit) - Lenovo B475e, B575e. Click Start, right-click my computer and select manage. In Device manager, click Network adapters. In Device manager, double-click 'Realtek PCIe GBE Family Controller'. Click the 'Driver' tab. Then you will see the driver version.
Now go to Application Pools panel, open the Edit Application Pool window by right-clicking on the website’s app pool and selecting Basic Settings and set .NET CLR version to No Managed Code:
Check if .Net Core Windows Server Hosting bundle is installed properly
Next step is to check whether the hosting bundle which we installed earlier is installed properly or not.
For this click on Modules(in IIS Manager) of your newly created website and search for AspNetCoreModule. If it is available, it indicates that IIS is now aware of how to run a .Net Core application.
You might be wondering what is Asp .Net Core Module?
- ASP.NET Core Module lets you run ASP.NET Core applications on IIS for what it’s good for i.e. security, manageability, and lots more
- On the other hand, ASP.NET Core Module lets you run ASP.NET Core applications using Kestrel for what it’s good at for example being really fast
- Thus it is getting the benefits of both technologies at once
- Asp .Net Core Module handles all incoming traffic to IIS and acts as the reverse proxy that knows how to hand the traffic off to your ASP.NET Core application
You may have noticed that when we published the code to a particular folder, a web.config was created in which you can see aspNetCore under Handler section as below. This is only used when deploying your application to IIS and It registers the AspNetCoreModule as an HTTP handler.
That is it.
Just load your IIS site and it should load just fine:
Now the application is hosted on IIS.
Net Core 20 Download For Windows
Hope it helps.